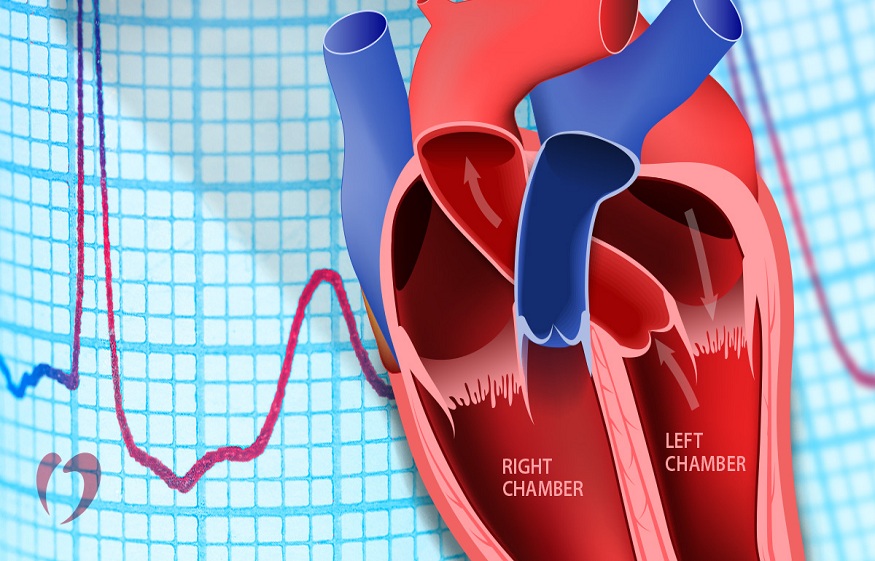
Heart block is an electrical block. It is different from the blockages in the blood vessels. The sinus node which is the natural pacemaker of the heart generates electrical impulses and these electrical impulses press through the upper chambers of the heart like a wave proceeding to the lower chambers through an electrical bridge. Electrical bridge is nothing but a cluster of AV nodes connecting the electrical activity from the upper chambers (the atria) and the lower chambers (the ventricles). In case of heart block there is an abnormality noticed in the electrical bridge and as a result the impulses that originate in the upper chambers cannot get down to the lower chambers. There are various degrees of heart block based on the extent to which the electrical impulses are slowed down while proceeding to the ventricles.
Statistically speaking, China is the country with the most cases of heart diseases, followed by India, which is one of the top destinations for medical tourism. Due to the fact that India is a hub for medical tourism, there are several specialized treatments available at various rates throughout the country, including heart specialists. Interestingly, Bangalore is touted to have hospitals with superior infrastructure, being the silicon valley of India. Thus, if on the lookout for a high quality heart specialist hospital in bangalore, one would be presented with various options depending on their budget.
Types of heart blocks-
First degree heart block- In this the electrical impulse does pass through to the lower chambers but is slower than usual. It takes more than a quarter of a second to proceed to the ventricles.
Second degree heart block- In second degree the electrical impulses get down to the lower chamber but not every impulse makes it to the ventricles. Thus causing a drop in the heartbeats. The rhythm of the heart gets irregular because the lower chamber doesn’t beat as fast as the pacemaker is driving the upper chambers.
Third degree heart block- This is also known as complete atrioventricular block. In this the impulse doesn’t get through the electrical bridge. No impulses reach the ventricles which is a serious condition. As lower chambers of the heart are the main pumping chambers. Due to absence of impulses they fail to pump blood or the natural backup of the ventricles starts generating impulses which are very slow and cause irregular heartbeats.
Causes: Anyone can have a heart block though elderly people are at a greater risk. Infants can be born with heart blocks in cases where they are affected with congenital heart disease or their mother suffers from autoimmune diseases like lupus. Though the causes in infants go undetected, there are few reasons that lead to heart blocks in elderly people.
- Damage incurred by the heart due to a heart attack.
- Coronary artery disease- It is a condition in which the coronary artery is damaged due to cholesterol containing deposits or inflammation.
- Cardiomyopathy- It is a heart disease in which there is progressive heart failure. The heart muscles become abnormally enlarged, thickened or thin, stiff and weakened leading to difficulty in pumping blood.
- Rheumatic heart disease- Rheumatic fever often leads to damage to the heart valve, this condition is called rheumatic heart disease. Children from poor countries with negligible access to antibiotics are at a much higher risk. This can lead to heart blocks resulting in heart failures.
- Heart Failure- When the heart fails to pump blood effectively to the rest of the body is termed as heart failure.
- Usage of some medicines like digoxin, beta-blockers and calcium channel blockers might lead to heart blocks.
- Trained athletes might have heart block due to vagus nerve as it slows the heart rate.
Symptoms-
Usually patients with first degree heart blocks do not show any significant symptoms. Patients with second and third degree blocks do show symptoms like lightheadedness, fatigue, tiredness, shortness of breath, fainting, chest pain, palpitation, irregular heartbeats.
Diagnosis-
Electrocardiogram is used to detect heart blocks. It records the electrical activity. By reading these patterns doctors can check for blocks.
Treatment:
In case of First Degree heart block no treatment is required unless there are symptoms. For second degree heart block the treatment is recommended depending upon the symptoms of the patient. Third degree heart block treatment is absolutely necessary. Now for treating any heart block initially the reason behind such heart block. For instance any person having electrolyte imbalance may face heart block which can be easily managed by balancing the electrolytes. Similarly if someone comes with an infection which has caused inflammation, treating the infection can relieve the heart block. Or in cases of some new medication which is causing irregular heartbeats as a side effect can be cured by changing the medications.
Ruling out all the underlying causes if the block still persists then a pacemaker can be attached by surgery.